The gearbox is an essential part of any vehicle. It is connected to the engine and transfers power to the wheels. If the gearbox fails, it is obvious that the vehicle no longer responds correctly to your requests. If the malfunction is too serious, the vehicle may even come to a standstill automatically. If the engine power no longer reaches the wheels, the wheels remain inactive and the car cannot move forward or backward.
Impeccable service
Boite de vitesses cassée ? Nous vous aidons à trouver et commander votre modèle
Everything you need to know about how a mechanical gearbox works
The manual gearbox is designed to be activated manually by the driver. This means that you choose when to engage a gear and are free to select the gear you feel is appropriate for the conditions you are driving in. Early BVMs were limited to 3 or 4 gears, but with mechanical developments, the standard has been increased to 5 or 6-speedor even 7 gears on the most powerful vehicles.
When starting, the wheels do not turn automatically because they need to receive a driving force. This is achieved by using the energy generated by the engine when the vehicle is started. Mechanical transmissions are coupled with a gear lever and a clutch pedal that contribute to this power transfer. When the clutch pedal is depressed, the clutch disc is pushed through the mechanism to the flywheel. This action simultaneously locks the gearbox and the engine, which continue to operate at the same speed. You can then select first gear or engage reverse using the gear lever. By releasing the clutch pedal smoothly while you press the accelerator pedal, you then allow the tyres to roll using the energy provided by the gearbox.
The power generated by the engine increases automatically when you accelerate. However, each gear range has a maximum speed associated with it, expressed in revolutions per minute (rpm). When the engine reaches the ceiling, the transmission system, and therefore the gearbox, no longer runs at the same speed. This can lead to engine exhaustion and more or less serious breakdowns. The clutch pedal and the gear lever must be used to shift to a higher range. With the clutch disengaged, you can engage the next gear.
The principle is the same for downshifting. If the engine is running too slowly when you are in a speed range that allows you to drive faster, there is a risk that the engine will stop running. As a result, it stalls. A lower gear must therefore be selected to keep the vehicle moving.
Gear ratios, also known as transmission ratios, are ratios or reduction coefficients of the engine force. Their function is to create variations that are transmitted to the wheel management system via a gear system.
The gear lever is connected to a linkage that transmits the commands to the transmission system. Older cars usually have a linkage with a linkage. The mechanism is operated by metal rods. However, linkages are most often operated by cables.
When you operate the gearshift lever, the linkage activates a fork that moves a shifter so that the selected gear is selected. In effect, the shifter engages (or clutches) the pinions (or gears) found on thesecondary drive shaft. When you are in neutral, this means that no gears are engaged. Theprimary shaft, on the other hand, continues to operate at the same speed as the engine through the action of the crankshaft. If there are three shafts in the system, an intermediate shaft connects the primary and the secondary. These transmission shafts rotate continuously thanks to the bearings. It should be noted that in the case of synchronised gearboxes, synchroniser rings adjust the gear speed to match the engine speed.
The differential is another essential component of this system. Placed between the wheels and the gearbox, it is responsible for distributing speed evenly to the front/rear and left/right wheels.
Any gearbox needs to be properly lubricated so that the gears can function properly. This is the role of thegearbox oil, the level of which must be checked regularly. In addition, a periodic oil change is necessary. This consists of replacing the dirty oil with a clean lubricant, bearing in mind that impurities in the gearbox oil can damage the mechanical parts. It is of course important to check the viscosity index of the oil before filling or changing. Generally speaking, 75W80, 75W90, 75W140 and 80W90 oils are suitable for manual gearboxes, but it is essential to refer to the maintenance booklet or seek professional advice.
Since it contains wearing parts, it is only logical that a mechanical gearbox can fail. There are a number of warning signs that should alert you long before the system is no longer in working order. In many cases, manual gearbox malfunctions are manifested by difficulties in shifting gears. You feel some kind of resistance that makes it difficult to select a gear or that prevents you from engaging a gear altogether. It is also common to hear a creaking noise. Even if you fully depress the clutch pedal, the gears can still creak. Loose gears are also a common problem. While you are driving along, the gear you are in jumps out of gear without you doing anything about it. Other symptoms, such as an oil leak or a burning smell, should not be overlooked.
Once you notice a change in the behaviour of your manual gearbox, it is important to address the problem quickly. Of course, you should not repair the gear box yourself, as this could lead to further damage. Instead, you should quickly make an appointment with a professional. In the case of minor faults, a repair is usually sufficient to restore the gearbox to its full performance. In more complex cases and in situations where a conventional repair is not possible, replacement is the best option.
Understanding the operation of an automatic gearbox
For many years, the automatic gearbox For many years, the automatic transmission (ATB) that first appeared in the 1920s was only available on top-of-the-range cars. However, it became more commonplace, first being offered as an option on some vehicle models and then becoming the standard transmission on others.
While mechanical gearboxes are mainly distinguished by the number of gears they carry, automatic versions are subdivided into different categories that influence their mode of operation and have consequences for the performance of the transmission system.
The single-clutch automatic gearbox: commonly known as a robotised gearbox, it is mainly used in city cars and cars with low power output. In reality, it is a manual gearbox to which the manufacturer has added actuators. These are managed by a computer box driven by a hydraulic or electrical system that allows you to switch between two modes. When you engage the automatic mode, the system automatically selects and engages the gears. When you select the impulse or manual mode, you manage the gear changes.
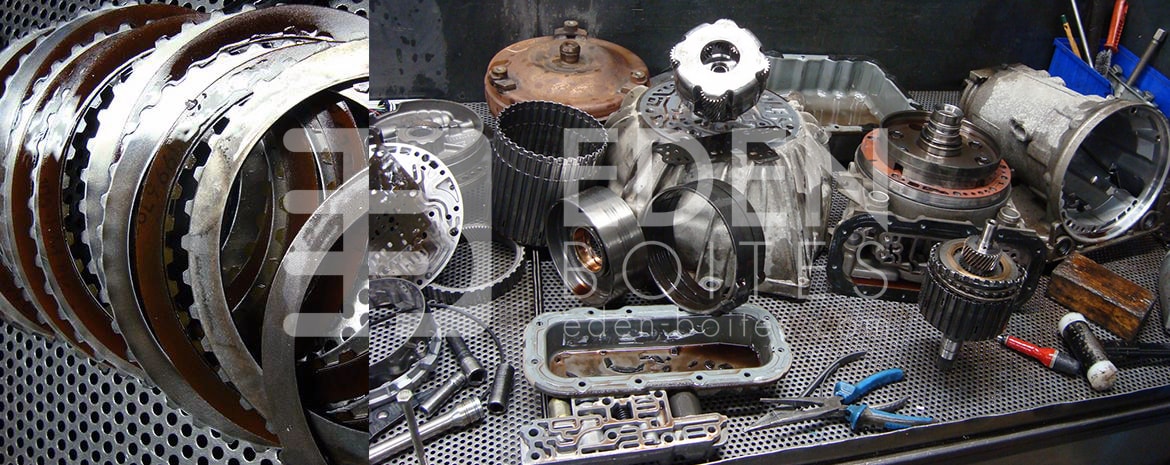

The dual-clutch automatic gearbox: the concept of a dual clutch corresponds to the presence of two half-clutches. One is associated with even gears while the other controls the odd gears. It is an improved version of the single-clutch automatic gearbox since hydraulic cylinders or electric motors control the pre-selection of gears. When first gear is engaged, the even-gear half gearbox pre-selects second gear, which is automatically engaged as soon as the odd-gear half gearbox is disengaged. As soon as the second gear is engaged, the third gear is preselected and so on. This makes gear changes quicker and smoother, eliminating jerky shifts and sparing you the need to break off acceleration while driving. The dual-clutch BVAs thus provide a comfortable driving experience and boost the car's performance.
The automatic transmission with hydraulic torque converter is halfway between the robotised version and the dual-clutch model. It has two propellers. The one attached to the BVA is lubricated by the propeller which is immersed in oil and connected to the engine. The converter isolates the BVA from the engine. When the speed at the input is different from the speed at the output, the converter reduces the torque so that the engine can continue to run independently of the transmission system.
The CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission) which is very common on two-wheelers is also available on many cars with moderate power. It is therefore common to find it on compact cars. With this type of automatic transmission, the number of gears is unlimited. The integrated mechanical system automatically regulates the torque and engine speed according to the driving conditions.
Like the manual gearbox, the automatic version is also coupled with a lever. However, it does not determine the choice of gears. Instead, the position of the lever corresponds to the driving mode, which is indicated by a letter or a number:
- P stands for Parking. When you park and select this mode, the wheels of your car are automatically blocked. However, it is not advisable to activate this mode if other vehicles are parked in close proximity to yours. A possible shock could damage the previously locked gears, which would cause anomalies;
- R stands for Reverse. In other words, this is the range to select before reversing;
- N or Neutral is the neutral position. By leaving the lever in this position, you allow the vehicle's wheels to turn freely as they are unlocked;
- D stands for Drive and is the position corresponding to forward motion. Logically, this is the position you use by default after starting. The gears change without your intervention, unless you have selected the pulse mode;
- L (Low) or 1 means that the transmission system uses only the first gear. This means that a very low gear is used. It is particularly relevant to activate this position when towing a broken down car or when going up relatively steep hills;
- 2 indicates that the selections will be limited to the first two gears. As you can imagine, it is more advantageous to switch to this mode when you need to drive at a moderate speed (driving on mountain roads, towing a heavy load, etc.)
Some vehicle models have additional driving modes:
- 3 sets the maximum range in third gear. This means that only the first three gears are used. This mode is very suitable for traffic in built-up areas;
- S stands for Sport mode. It is therefore suitable for sporty driving that involves smooth gear changes. Shifting up is always done at high engine speed. Braking during downshifting tends to be abrupt;
- W or Winter is the snow mode. The car is started in second gear and not first, so that the risk of skidding is reduced.
Automatic gearboxes are equipped with an electronic control unit that distributes the oil under pressure to ensure the correctness of gear changes. This means that you don't need to intervene, allowing you to concentrate fully on driving your car. However, this comfort is reduced when the BVA fails. Faults can be recognised by jerking when starting or changing gears. You may also hear abnormal noises, oil from the gearbox may spill onto your driveway or you may smell something burning. Other signs may be present. It is therefore important to keep an eye on the behaviour of your BVA and to react as quickly as possible to any loss of performance.
How to optimise the life of your gearbox?
Repairing a faulty box can lead to a hefty bill. Rest assured, many breakdowns can be prevented with good habits and reflexes. The aim is to preserve the gearbox in order to ensure its longevity.
First of all, check the transmission fluid level regularly. Since it is the oil that lubricates the various components to ensure that the driving force is received by the wheels, it must always be sufficient. If the oil level is lower than the recommended level, refill the oil, taking into account the viscosity of your type of gearbox. In theory, automatic transmissions should be changed every 60,000 to 100,000 km. Except in special cases, mechanical gearboxes generally do not require an oil change. However, manufacturers' recommendations vary and are therefore the absolute references. If you have any doubts, consult a professional who will confirm whether or not your gearbox should be changed.
Secondly, always pay attention to the behaviour of your car. Particular attention should be paid to the gearbox, as major malfunctions are often the result of faults that initially seemed harmless. If you notice any alarming signs, take action without delay. In addition to the symptoms mentioned earlier, the warning lights also provide information on the status of the transmission system. In fact, they light up to indicate anomalies that you should take into account as soon as possible. Bear in mind that the longer you delay in reacting, the more serious the fault is likely to become and the more complicated repairs will be.
Your driving style can also increase or decrease the life of the gearbox. With a manual gearbox, for example, it is essential to press the clutch pedal down firmly before operating the gear lever. Otherwise, you risk breaking the mechanism and the system will no longer respond correctly to your commands. If you are using an automatic transmission, always check the mode you have selected with the lever. In general, a smooth driving style is preferable to an aggressive one as it prevents you from forcing the gearbox, which will weaken it.
Regular servicing of the vehicle may seem obvious to some drivers, while others neglect this step. The exact frequency is specified in the service booklet, but it usually ranges from 15,000 km to 30,000 km. Overhauls are important because they check all the systems that keep your car running smoothly. The gearbox is no exception to the rule. The professional will be able to detect all the defects, even minor ones, which will prevent you from facing advanced anomalies. The oil level, the sensor settings, the fixing of the linkage... everything will be checked with the greatest care. Take note of the garage's warnings and carry out the necessary repairs as soon as possible to prevent the gearbox problem from getting worse.
When replacement parts are required, be aware of the part numbers of the replacement components. Compatibility is essential!
How to react to a gearbox anomaly?
You may be tempted to carry out the repair in your own garage, without the intervention of a professional. Indeed, a few searches on the internet will allow you to find tutorials that explain how to detect and repair gearbox failures. However, these instructions are generic and not exhaustive. In other words, the information you will find will give you the basics but that's all! You will therefore need to go through a craftsman who has all the necessary skills to make a diagnosis, because that is where any repair starts.
Going to a professional does not mean that you can do absolutely nothing. On the contrary, you can help identify the fault by noting the symptoms of malfunction as accurately as possible. What makes you think there is a problem with your gearbox? How long have the anomalies been occurring? Have you noticed a specific factor that triggers the signs of failure (starting up, accelerating, reaching a certain mileage, engaging a particular gear, etc.)? However, you should not feel guilty if you do not manage to provide many details.
Once you have explained the problem you are experiencing with your gearbox to the professional who will be carrying out the repair, he can begin the diagnosis. This usually begins with a visual inspection. Each component is carefully assessed to determine its condition and whether it needs to be repaired or replaced. Tests may also be carried out to check the electronic systems.
If these initial checks do not produce convincing results, the professional may consider removing the gearbox. In other words, he will remove it from the rest of your car by dismantling it. The operation is extremely delicate because there are several steps to follow, depending on the characteristics of your transmission system. The order in which the fasteners are to be removed, the precautions to be taken to avoid breakage of the various components... all this requires know-how that only professionals have. Add to this the fact that the choice of tools is not made at random. It's all about precision!
It is difficult to make a diagnosis with certainty unless you have a thorough knowledge of car mechanics. The same sign can indicate different types of anomalies. Let's say you've noticed a squeaky gearbox. This symptom may be due to a lubrication problem (low oil level or clogged lubricant). It is also possible that the gears are broken or that screws are incorrectly tightened, causing play in the mechanical components. Again, these are just examples of possible failures. The choice of repair method will therefore depend on the exact cause of the malfunction, which is why you should never do it yourself. If you make a mistake, you will not solve the problem. On the contrary, you risk making it worse, which will cost you more when you decide to leave it to a qualified professional.
In cases where the gearbox has suffered significant damage, the repairer may recommend a complete replacement. The absolute rule of thumb before purchasing is to formally identify the part number of the faulty gearbox. This is a code that the car manufacturer engraves on the oil pan or mentions on a label. Your garage will be able to provide you with the reference number, but you can also use the vehicle registration document, which defines the characteristics of your car, to find out the exact type of gearbox that is suitable.
You then have two options. The first is to ask your garage to buy the spare part. He will add it to the bill, but beware that a commission is usually charged, which will increase the amount you have to pay for the repair. The second option is to buy the necessary part yourself. Based on the part number you have been provided with, you only have to go through a shop that specialises in gearbox sales. EDEN BOITES is the European market leader. You are sure to find what you need, at highly competitive prices without neglecting quality. You can order a used gearbox or choose a standard exchange gearbox. In the event that the reference you are looking for is not available in stock, do not hesitate to request a quote for the reconditioning of your defective gearbox.
Do not hesitate to consult the articles in the blog which will help you understand the specificities of gearboxes according to the make and model of vehicle you drive. You will also find many expert tips.




